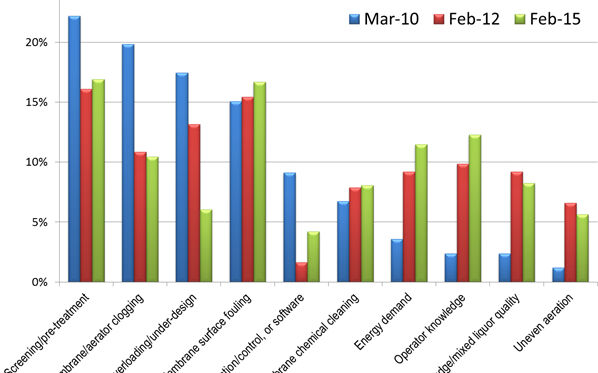
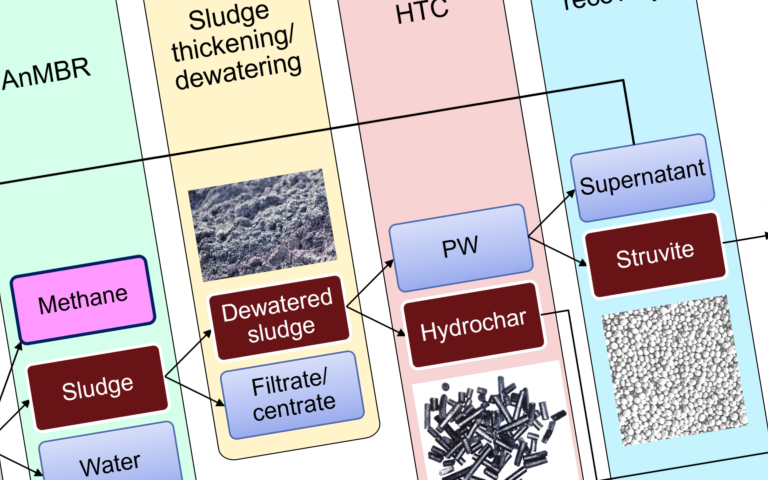
Key MBR operation and maintenance parameters – biological side

Biological process parameters in MBRs
The biological process parameters do not differ from those of a classical activated sludge (CAS) process, though MBRs are able to operate at longer solids retention times. The key parameters for activated sludge-based technologies comprise:
- the hydraulic retention time HRT, or θw: the residence time of water in the reactor, given by the ratio of the tank volume V to the liquid flow Qw
- the solids retention time (or sludge age) SRT, or θx: the residence time of sludge in the reactor, given by the ratio of the tank volume to the sludge wastage rate Qw
- the food to micro-organism ratio, F:M: the ratio of substrate S (the organic matter, represented by the BOD or COD) to biomass (assumed to be represented by the volatile fraction of the mixed liquor suspended solids, MLVSS or X’). So, F:M = SQw/(VX’)
- the sludge yield, Y’: the ratio of cells (biological sludge) formed to substrate consumed.
Because MBRs operate at a longer SRT than CAS processes, the mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS, or sludge solids) concentration is higher. This then reduces the F:M ratio, which means that there is less substrate (or food) available for the micro-organisms. Consequently, the waste sludge generated is reduced.