Pollutant removal in MBRs
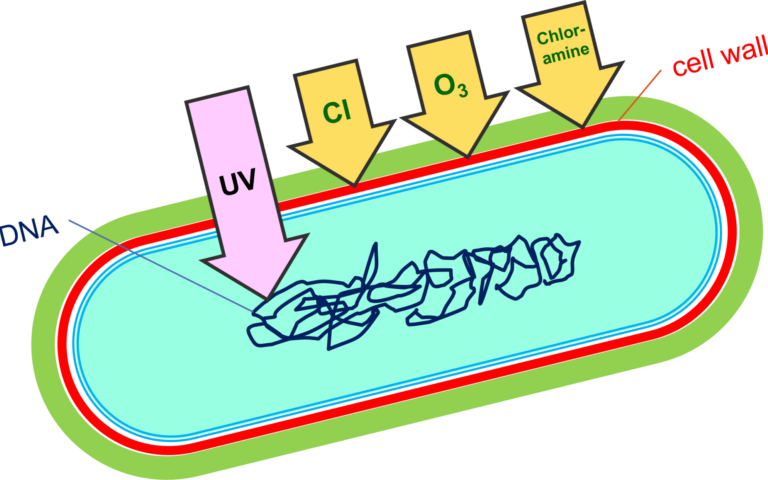
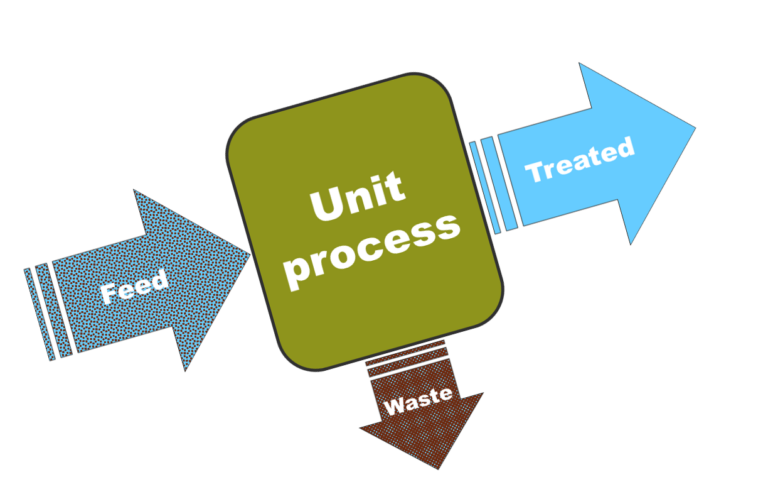
Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) achieve increased removal of most pollutants compared with the conventional activated sludge process.
This is because, among other reasons, the mixed liquor is filtered through a membrane with an effective pore size of <0.1 µm.