Fundamentals of MBR design
Membranes and biotreatment
The design of a membrane bioreactor system largely relates to:
- the configuration of the membrane,
- the membrane separation process, and
- the biotreatment process.
Fundamentals of MBR design − the immersed membrane bioreactor (iMBR) process
1. Membrane separation process configuration
Membrane configuration concerns the geometry of the membrane (hollow fibre, flat sheet or tubular) and the direction in which the water flows through it (in-to-out or out-to-in).
The membrane separation process configuration concerns the placement of the membrane module in the overall MBR process, i.e. either inside or outside the tank.
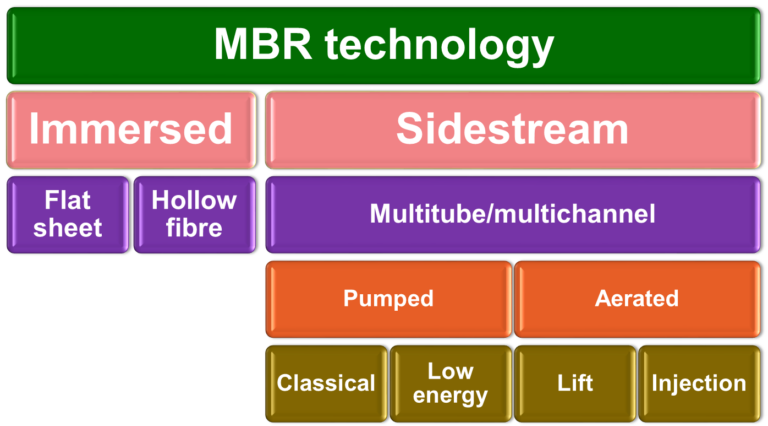
2. Biotreatment process configuration
The biotreatment process configuration determines the biochemistry and, therefore:
- which pollutants are removed (organic carbonaceous materials, ammoniacal compounds and nutrients), and
- which products are formed (carbon dioxide or methane, nitrate or nitrogen, etc).
Biotreatment using air is referred to as ‘aerobic treatment’, leading to carbon dioxide as the main carbon-based product. In the absence of air, biotreatment is termed ‘anaerobic treatment’, which yields methane.
Biotreatment processes can be configured either as ‘fixed film’ or ‘suspended growth’. An MBR is a suspended growth process, based on the classical activated sludge (CAS) process but with membrane separation rather than sedimentation of the retained biological solids.
Membrane technology is integrated with a biological process either as a filter for retaining the biomass, as in an MBR, or as a diffuser for introducing air or oxygen in the molecular or bubbleless form, as in a membrane aerated biofilm reactor or MABR.
Membrane filtration may also be used downstream of a CAS for removing residual solids. In this case it is not integrated with the biological process and may be referred to as a 'polishing' step.
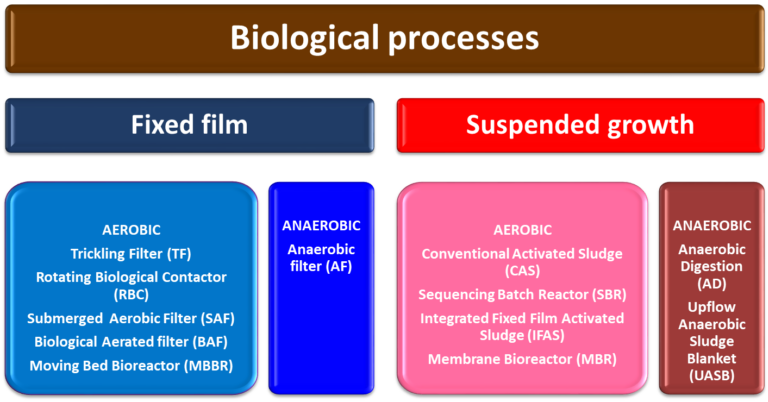
Membrane integration in biological treatment processes
Further elements of design comprise pretreatment (screening and, for some applications, clarification) and post-treatment (generally either disinfection or desalination).







