The Top 20 Largest MBRs in the World?

Simon Judd
Simon Judd is author of The MBR Book (Elsevier, 2010).
Note: this feature was written in July 2011. For the latest lists of largest plants see: Largest membrane bioreactor plants (over 100 MLD) – Worldwide.
1. Introduction
In October 2009, I was the grateful and enthusiastic recipient of a list of what was thought to be the 20 largest MBRs in the world at that time. The peak daily flow capacities on that list ranged from 30 to 100 MLD, with the total capacity being just over 1,000 MLD. 16 of the top 20 installations were fitted with GE’s Zeeweed technology, though the largest − Origin Water’s Wenyu river plant in Beijing, commissioned in late 2007 − was based on Asahi Kasei membranes.
Fast forward to the future − to April 2012 − and it appears the list will have changed somewhat. GE still dominates, occupying 12 of the places on the list. It is anticipated there will be nine MBRs of 100 MLD or more peak daily flow capacity by April 2012, compared with just the one in October 2009, and the total peak capacity provided by the listed plants is around 1,900 MLD.
2. Bigger and bigger…
It’s obviously not the first time it’s been observed that MBR plants are increasing in size, but the speed with which it is happening is perhaps surprising. However, the requirements of individual countries, and China in particular, are becoming ever more pressing given the increasing scarcity of freshwater and the stringency of the environmental legislation promulgated to tackle this.
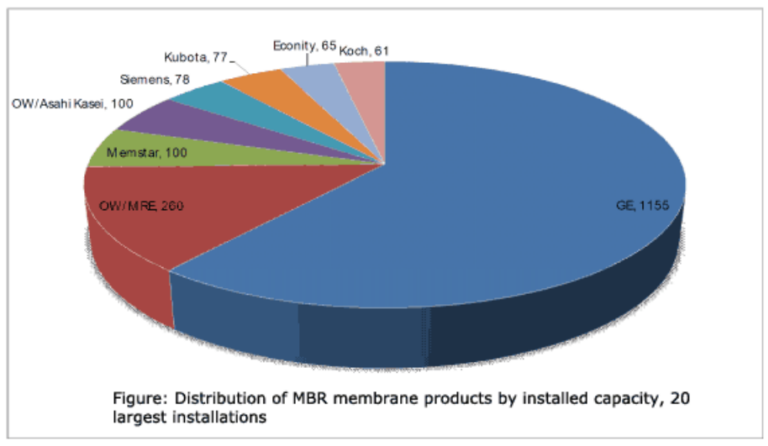
Whilst GE still provide ~60% of both the number of plants and installed peak daily flow capacity, it is notable that there are seven other membrane product providers contributing the remaining eight plants on the list. Of these seven suppliers, two are from outside South-East/East Asia. There are also plans for future large MBR plants employing other MBR membrane products, with contracts secured for plants >10 MLD in capacity for installations based on MICRODYN-NADIR (at Ji’An in Jiangxu) and elsewhere for air-lift Norit tubular membranes.
A 30-MLD industrial effluent plant based on Motimo membranes was installed in Tianjin in 2007, and the 57-MLD Toray plant at Yas Island in the UAE is nearing completion (with a larger plant planned for Najran, KSA). There will therefore be at least 12 MBR membrane product suppliers with one or more large flagship MBR plants operating within the next two to three years, eight of them being from South-East/East Asia.
3. Future trends
In any event, the trend in large plants is likely to continue, with more >100 MLD PDF capacity MBR plants already planned. The GE US plants at Frederick County (132 MLD PDF) and Cox Creek (114 MLD PDF) are due to be commissioned in 2013 and 2015 respectively, the contracts for the Riverside and Visalia plants in California, peaking at 182 and 167 MLD respectively, having recently been awarded to the same company.
There will doubtless be further large Origin Water installations in China, where five of the listed plants are based, compared with six in North America. In the four years between 2006 to end 2009, at least 20 MBR plants of >10 MLD peak capacity were installed in China, providing a total installed capacity of 760 MLD. Moreover, five of these plants (78 MLD installed capacity in total) are dedicated to petrochemical effluent treatment − which perhaps reflects the scale of industrial activity in China and the associated pollution abatement challenge the country faces.
It is sobering to think that it was only a decade-or-so ago that the Kubota plant at Swanage in the UK was still heralded as the largest in the world − at just under 13 MLD peak flow. There is only a passage of eight years between the commissioning of the Swanage plant and that of the 100 MLD Wenyu river plant.
4. Largest 20 MBRs?
| Installation | Supplier | Date | ADF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
PDF: Peak daily flow | ||||
| Brightwater, WA | GE | 2011 | 170 | 117 |
| Qinghe, China | OW/MRC | 2011 | 150 | 150 |
| North Las Vegas, NV | GE | 2011 | 133 | 95 |
| Yellow River, GA | GE | 2011 | 111 | 69 |
| Shiyan Shendinghe, China | OW/MRC | 2009 | 110 | 110 |
| Aquaviva, Cannes, France | GE | 2012 | 106 | 59 |
| Busan City, Korea | GE | 2012 | 100 | 100 |
| Guangzhou, China | Memstar | 2010 | 100 | − |
| Wenyuhe, Beijing, China | OW/Asahi Kasei | 2007 | 100 | 100 |
| John’s Creek, GA | GE | 2009 | 94 | 42 |
| Awaza, Turkmenistan | GE | 2011 | 87 | 69 |
| Jordan Basin WRF, UT | GE | 2012 | 79 | 53 |
| Beixiaohe, China | Siemens | 2008 | 78 | − |
| Al Ansab, Muscat, Oman | Kubota | 2010 | 77 | 55 |
| Cleveland Bay, Australia | GE | 2009 | 75 | 29 |
| Broad Run WRF, VA | GE | 2008 | 71 | 38 |
| Christies Beach, Australia | GE | 2011 | 68 | 27 |
| Gongchon, Korea | Econity | 2012 | 65 | 65 |
| Lusail, Qatar | GE | 2011 | 61 | 61 |
| Aquapolo, Sao Paulo, Brazil | Koch Membrane Systems | 2012 | 56 | 56 |
Footnote (2012)
Since this article was published, I’ve been informed that there’s another GE plant located at Nizhnekamsk, Tatarstan in Russia which has an ADF of 50.4 MLD, for treating effluent from the Taneco oil refinery site. Unless the PDF is >25% higher than the ADF, it doesn’t quite make the Top 20. However, it should be up and running by April 2012 and, by my reckoning, could then be the largest industrial effluent MBR in the world.
I’ve also had word of the status of some of the Econity Korean plants. A large projected plant − the Siheung & Ansan project (73 MLD) − has been cancelled, but the Songsan Green City project, Korea (84 MLD) has been secured, planned for 2015 start up. Also, GE’s Busan City plant may have a total capacity of 100 MLD when complete, though my understanding is that this won’t be for a few more years.
See the latest list of Largest plants worldwide