Biological processes
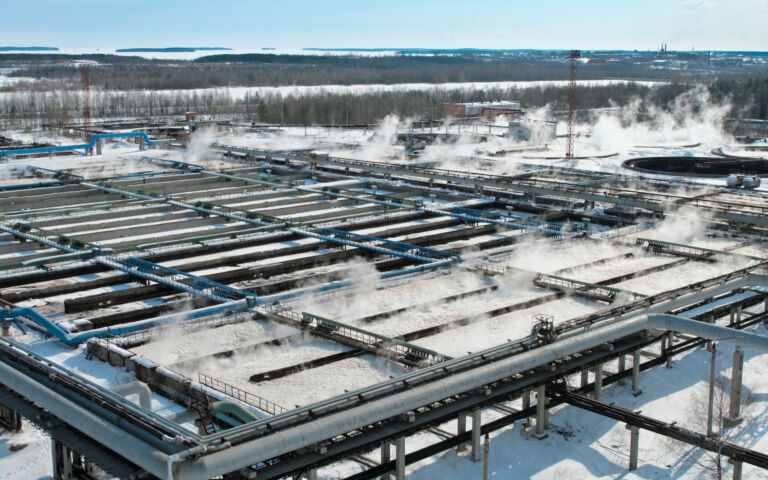
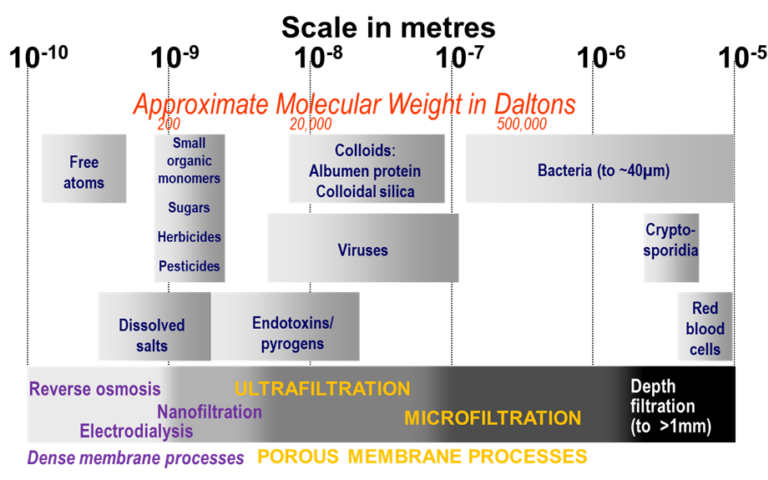
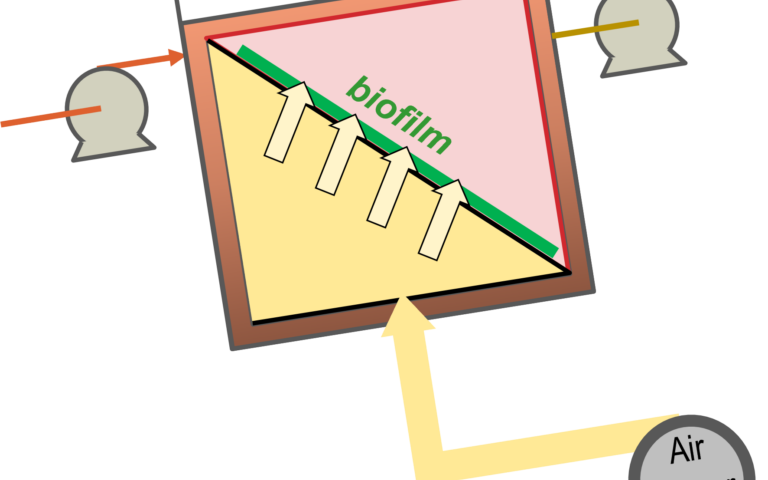
Biological treatment is used for removing organic carbon and nutrients (N and P), and can be aerobic, anoxic or anaerobic according to whether or not oxygen is present and its chemical form (molecular oxygen or oxyanion).
Aerobic processes are the mostly widely employed, most commonly as the conventional activated sludge (CAS) process. The CAS is the most prevalent example of a 'suspended growth' biological process.