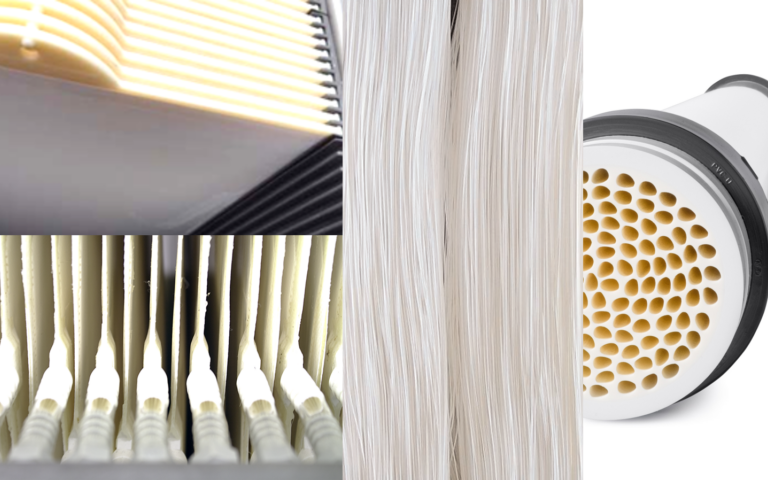
Introduction to MBRs
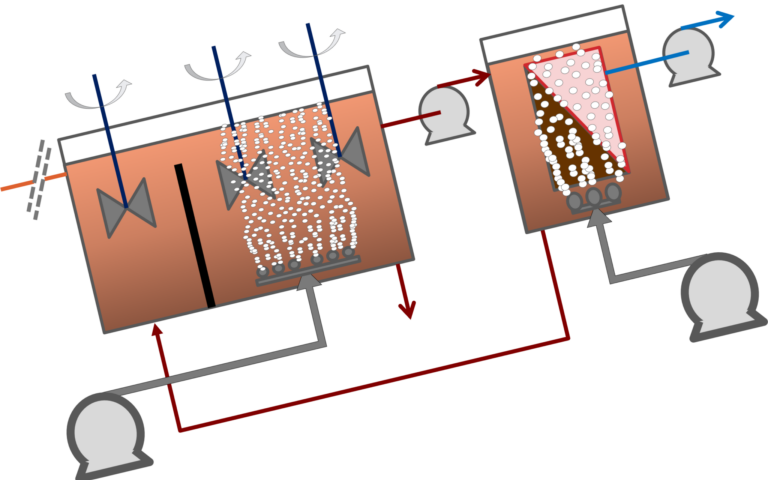
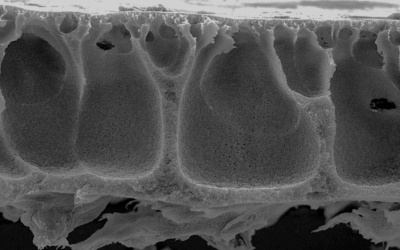
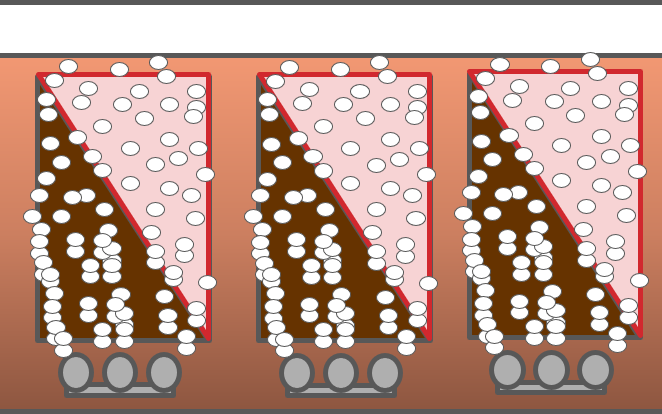
MBRs represent an enhancement of the conventional activated sludge process (CAS), where the usual secondary clarification step is replaced by membrane separation. This offers a number of advantages, including operation at longer solids retention times without impairment of the treated water quality.