Classical wastewater treatment
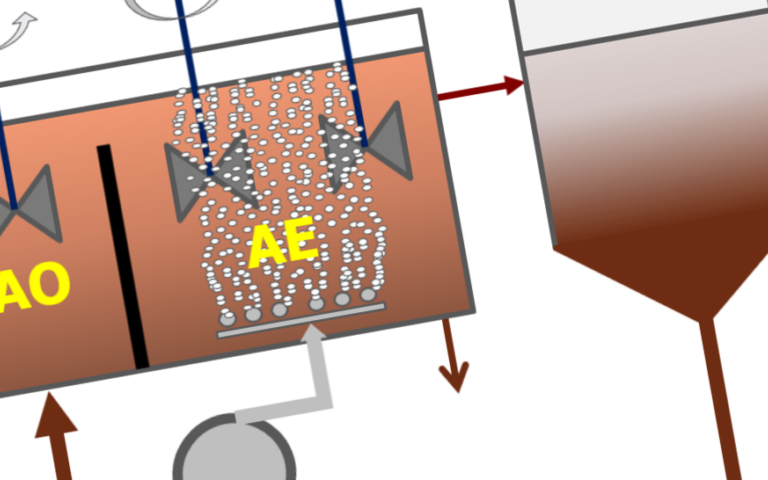
The CAS process comprises a biological tank, in which the aerobic biodegradation of the organic carbon and amino compounds takes place, followed by a sedimentation tank (secondary clarifier).
Your web browser is out of date.
Update your browser for better security, speed and to get the best experience on this website.


Biological treatment is used for the removal of organic carbon and nutrients (N and P) removal. They can be aerobic, anoxic or anaerobic. Aerobic processes are the widely employed, most commonly as the conventional activated sludge (CAS) process.
Key biological process parameters are the hydraulic and solids retention times, which determine the mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) concentration and food to micro-organism (F:M) ratio.
The CAS process comprises a biological tank, in which the aerobic biodegradation of the organic carbon and amino compounds takes place, followed by a sedimentation tank (secondary clarifier).

The biochemical action of a biological process is dependent on whether oxygen is present, and in what form. Oxidative ‘aerobic’ processes require dissolved oxygen to convert organic carbon to carbon dioxide and ammonia to nitrate.
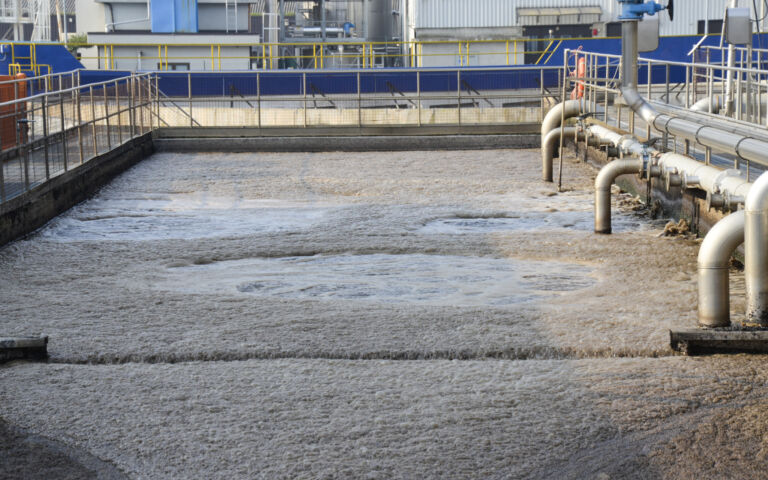

Biological process parameters for MBRs are no different to those of a classical activated sludge (CAS) process, though MBRs are able to operate at longer solids retention times and retain all the biomass.
Nitrate formed from nitrification of ammonia can be converted to nitrogen gas by biochemical reaction with organic carbon. This is an example of an 'anoxic' process and known as ‘denitrification’.

MBR sludge is characterised by two different types of microorganism - those responsible for carrying out biochemical functions and pathogens.

Sludge rheology relates to how it flows. This is in turn characterised by its viscosity, which is defined as the relationship between the shear stress and the shear rate.